Types Of Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology
Although adenomas are benign lesions they can undergo malignant transformation to hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. The incidence of hepatic adenomas is unknown with studies showing migration from the classically described female predominance related to the use of oral contraceptives to an increased prevalence in men particularly recognizing that obesity and metabolic syndrome are emerging risk factors for adenomas 18.
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
However only few papers have comprehensively described the entire spectrum of atypical and uncommon imaging features.

Types of hepatic hemangioma radiology. At ultrasonography US hemangiomas classically appear as focal homogeneous hypovascular echogenic lesions. Other unusual imaging patterns. Color Doppler sonographic evaluation will show increased flow.
Variants and atypies Giant haemangioma. Fluid-fluid level containing hepatic haemangioma. It is the most common liver tumour and is usually asymptomatic and diagnosed incidentally on radiological imagingLiver hemangiomas are thought to be congenital in origin.
They are termed giant hemangiomas when they exceed 4 cm in. On dynamic contrast-enhanced CT or MR imaging peripheral globular enhancement and a centripetal fill-in pattern with the attenuation of enhancing areas identical to that of the aorta and blood pool. A cavernous liver hemangioma or hepatic hemangioma is a benign tumour of the liver composed of hepatic endothelial cells.
The classic diagnostic findings for hemangioma are as follows. Patients affected by hemangioma usually have their tumor diagnosed by ultrasound abdominal examination for a not well defined pain but pain persist after. In patients with a giant liver hemangioma observation is justified in the absence of symptoms.
On sonography homogeneous hyperechogenicity or hypo- or isoechogenicity. The lesion may appear hypoechoic. Hemangiomas present a diagnostic challenge because they can be mistaken for hyper-vascular malignancies of the liver and can coexist with and occasionally mimic other benign and malignant hepatic lesions including focal nodular hyperplasia hepatic adenoma hepatic cysts hemangio-endothelioma hepatic metastasis and primary hepatocellular carcinoma 1 2 3.
The hemangioma is the most common solid lesion of the liver. In all hepatic hemangiomas 23 lesions were typical type mean 166 mm with peripheral nodular early enhancement progressing centripetally to complete n 8 or incomplete n 15 central enhancement and nine lesions were high-flow type mean 96 mm with uniform enhancement at the arterial phase 8 22. Hepatic adenoma is traditionally considered the most frequent hepatic.
Large hemangiomas are often heterogeneous 10. Typically incidentally found hemangiomas are smaller than 3 cm and occur in the posterior segment of the right hepatic lobe 4. A liver hemangioma he-man-jee-O-muh is a noncancerous benign mass in the liver.
Giant hepatic hemangioma flash filling hepatic hemangioma. This consists of several haemangiomas distributed in the hepatic parenchyma. Although malignant transformation is rare for this reason surgical resection is advocated in most patients with presumed adenomas.
The imaging techniques that can single out liver hemangioma from other types of tumors include. Flash filling hepatic hemangiomas also known as flash filling hepatic venous malformations are a type of atypical hepatic hemangioma which due to its imaging features often raises the concern of a malignant process rather than a benign one. Giant liver hemangiomas are defined by a diameter larger than 5 cm.
Hepatic haemangioma with fatty infiltration. Liver hemangiomas are readily demonstrated by abdominal ultrasonography computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. On unenhanced CT hypoattenuation similar to that of vessels.
Most cases of liver hemangiomas are discovered during a test or procedure for some other condition. Hepatic haemangioma with surrounding regional nodular hyperplasia. Cystic or Multilocular Hemangioma.
Therefore radiologists must know the typical and atypical imaging findings of this lesion in order to reach a correct diagnosis and avoid diagnostic errors. Several subtypes exist including the giant hepatic hemangioma which can cause significant. Association with Other Lesions.
Up to 16 of all hepatic. Hepatic cavernous hemangioma accounts for 73 of all benign liver tumors with a frequency of 04-73 at autopsy and is the second most common tumor seen in the liver after metastases. People who have a liver hemangioma rarely experience signs and symptoms and typically dont need treatment.
These haemangiomas may be. In some cases such as large heterogeneous hemangiomas calcified hemangiomas pedunculated hemangiomas or hemangiomas developing in diffuse fatty liver a specific diagnosis can be established with imaging especially magnetic resonance imaging. A liver hemangioma is made up of a tangle of blood vessels.
Infantile hepatic hemangiomas have a variable sonographic appearance and can be either hypoechoic or hyperechoic or may display mixed echogenicity with prominent vascular channels. The two most common liver lesions causing hepatic hemorrhage are HA and HCC. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound high-frequency sound waves are sent through body tissues and the echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photos.
Other terms for a liver hemangioma are hepatic hemangioma and cavernous hemangioma. Hepatic haemangioma with capsular retraction. The appearance varies according to the background liver parenchyma.
Up to 16 of all hepatic hemangiomas calcified hepatic hemangioma. Subtypes typical hepatic hemangioma atypical hepatic hemangioma 912 giant hepatic hemangioma flash filling hepatic hemangioma. It consists of a cavernous haemangioma measuring over 4 cm in diameter 4.
On T2- and heavily T2-weighted MR imaging hyperintensity similar to that of cerebrospinal fluid.
 Hemangioma Of The Liver Liver Tumor Liver Problems
Hemangioma Of The Liver Liver Tumor Liver Problems
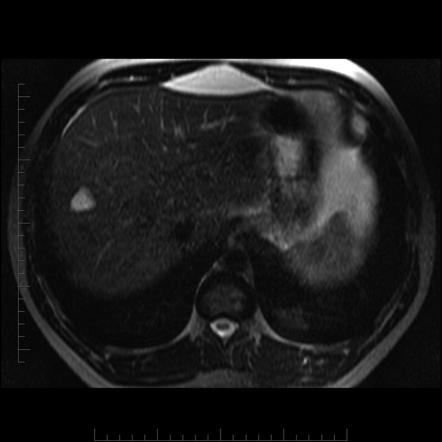 Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
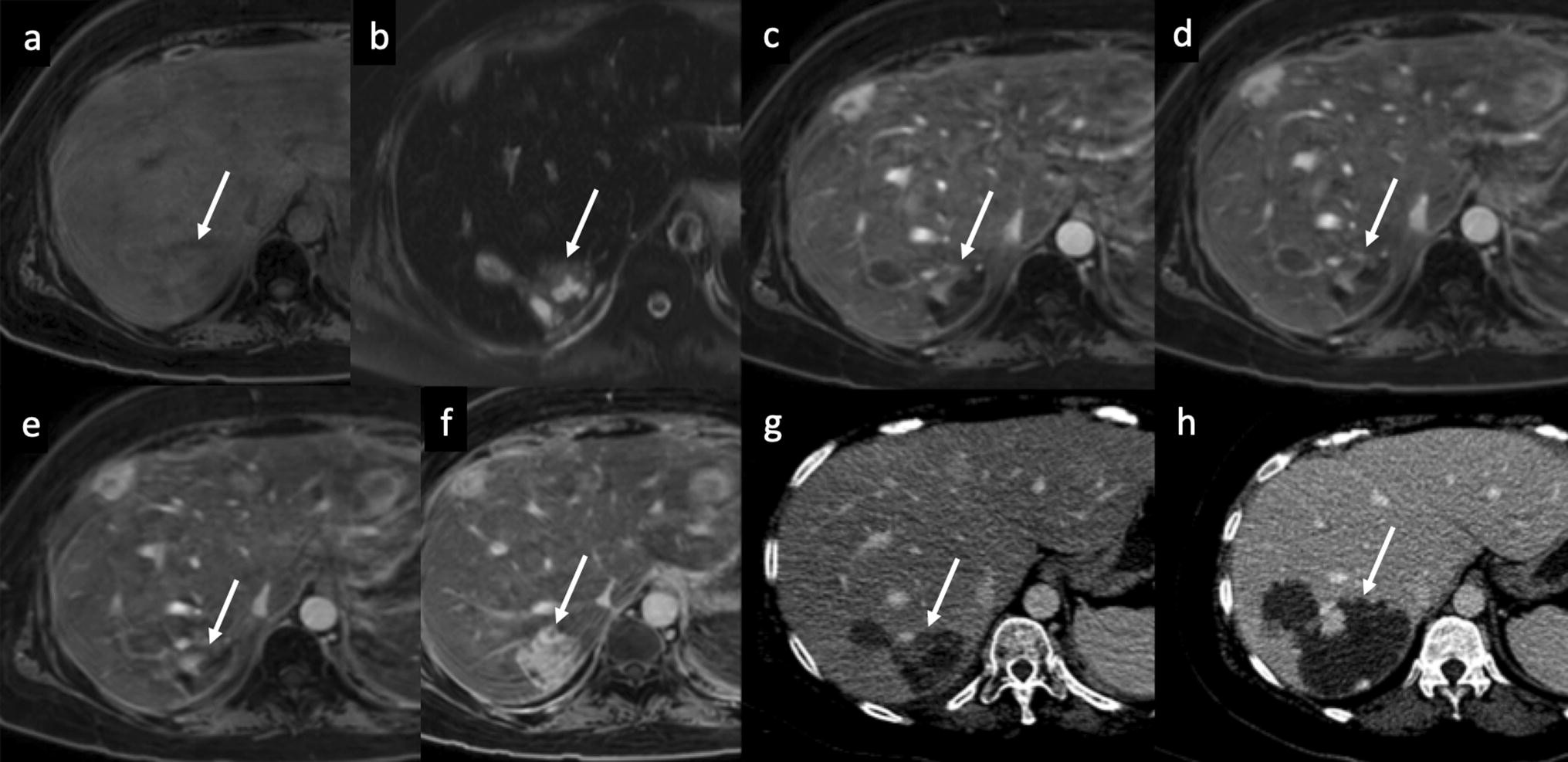 Figure 9 Imaging Of Hepatic Hemangioma From A To Z Springerlink
Figure 9 Imaging Of Hepatic Hemangioma From A To Z Springerlink
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
 Radiological Classification Of Infantile Hepatic Hemangioma Download Scientific Diagram
Radiological Classification Of Infantile Hepatic Hemangioma Download Scientific Diagram
 Hepatic Hemangioma Pitfalls Mimics Part I Youtube
Hepatic Hemangioma Pitfalls Mimics Part I Youtube
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
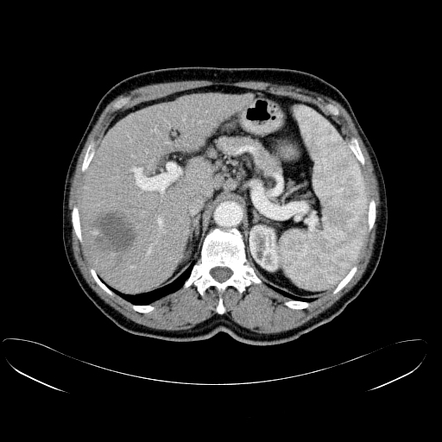 Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Differentiation Between Simple Cyst And Hepatic Hemangioma Utilizing T2 Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Gradient Echo B Ffe Technique
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
 Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay Iconographic Essay Unusual
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay Iconographic Essay Unusual
 Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Hepatic Hemangioma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
 Focal Nodular Hyperplasia Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Liver Anatomy
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Liver Anatomy
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
Cavernous Liver Hemangioma Wikipedia
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
Unusual Presentations Of Hepatic Hemangioma An Iconographic Essay
